Decoding New Age Market Accounts: How India’s Fintech & Banking Giants Are Reshaping Transaction Flows
"A Human-Centric Look at the Smart Account Structures Powering India’s Digital Economy—from Escrow 2.0 to API Banking, CBDCs, and Beyond"
Introduction India’s fintech and banking landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, and at the heart of this evolution are “New Age Market Accounts.” These aren’t your average current or savings accounts. Instead, they are built specifically to serve digital businesses, gig platforms, lending companies, and high-velocity marketplaces.
In our earlier blog, we explored “The World of Escrow”, a next-gen innovation enabling secure and automated fund flows for marketplaces and high-value deals. This post expands on that theme, diving deeper into the wide range of programmable, API-powered account types now offered by banks and fintechs.
The data presented here is derived from:
Product sheets and partnership updates from ICICI, Axis, Yes Bank, HDFC Bank, and IDFC First Bank
Fintech websites like RazorpayX, Cashfree, Open, and Zolve
RBI’s CBDC pilot documentation and circulars
Insights shared by the World Economic Forum on embedded finance trends.
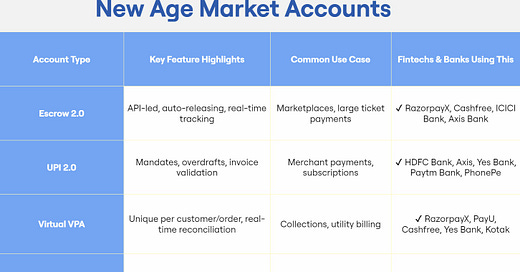
1. Escrow 2.0 – Real-Time Trust for Marketplaces Escrow 2.0 is an automated, API-triggered fund release system. It's a secure way to ensure that money moves only when defined milestones (like delivery or service completion) are met.
Key Features: Real-time tracking, API integration, conditional release logic
Use Cases: High-value transactions, marketplaces, B2B deals
Examples: RazorpayX, Cashfree, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank
2. UPI 2.0 – Making Payments Smarter, Not Just Faster UPI 2.0 adds new layers like mandates (scheduled debits), overdrafts (credit feature), and invoice validation, making UPI robust enough for commercial and recurring use.
Key Features: Scheduled payments, credit integration, invoice-level control
Use Cases: Subscription models, EMI collections, merchant invoicing
Examples: HDFC Bank, Axis Bank, Paytm Bank, PhonePe
3. Virtual VPA – Unique IDs for Better Reconciliation Each payment gets a dynamic, transaction-specific UPI ID, helping platforms instantly track and reconcile incoming funds per customer or invoice.
Key Features: Dynamic VPAs, real-time reconciliation, better audit trail
Use Cases: Utility bill payments, insurance premiums, EdTech and healthcare billing
Examples: Razorpay, PayU, Kotak Mahindra Bank, Yes Bank
4. Pooled/Nodal Accounts – Powering Aggregators These accounts enable platforms to pool customer funds in a ledgered, regulated manner. Common among e-commerce, ride-sharing, and gig platforms.
Key Features: Platform-wide pooling, ledger-level tracking, compliant fund segregation
Use Cases: Gig economy payouts, affiliate marketplaces, app-based commerce
Examples: Amazon Pay, Flipkart, Ola, Swiggy (via Yes Bank, ICICI Bank)
5. CMS 2.0 – Tech-Powered Treasury Automation Cash Management Services (CMS) have been modernized to integrate directly with ERPs and APIs. This enables automated collections, vendor payouts, and real-time dashboards.
Key Features: ERP/CRM/API sync, payment routing, reconciliation engines
Use Cases: Corporate collections, vendor management, retail franchise ops
Examples: HDFC SmartHub, ICICI InstaBiz, Axis CMS
6. Tokenized Money & CBDC – Programmable Currency is Real As part of RBI’s pilot projects, banks are experimenting with tokenized money and digital rupees. These enable programmable disbursements, like targeted government payouts.
Key Features: Controlled distribution, token-based transfers, government traceability
Use Cases: Subsidies, corporate vouchers, programmable employee benefits
Examples: HDFC Bank, Yes Bank, IDFC First Bank (RBI pilot banks)
7. API Banking – Developer-First Financial Infrastructure APIs enable fintechs and SaaS companies to plug banking into their apps without being a bank themselves. This powers account creation, payments, and more.
Key Features: Ready-to-use banking stack, full integration toolkit, real-time APIs
Use Cases: Fintech products, SME tools, embedded finance
Examples: Open, Zolve, Jupiter (partnered with Axis, ICICI, Yes Bank)
8. Lending + Escrow + UPI – Smart Lending Infrastructure This bundled structure ensures that lending platforms deduct EMIs via AutoPay, use escrow for traceability, and collect payments using UPI. It brings transparency to digital lending.
Key Features: Escrow-backed disbursals, automated repayments, real-time visibility
Use Cases: BNPL platforms, P2P lending apps, micro-lending solutions
Examples: KreditBee, LazyPay, Navi (via SBM Bank, IDFC First)
Conclusion: Invisible but Essential Infrastructure These new-age accounts operate behind the scenes, yet they are foundational to India’s fast-growing digital economy. Whether you're a startup founder, a corporate treasurer, or a product leader, understanding how these account types work can help you build scalable, compliant financial systems.
As we move forward, we’ll continue this series with deep dives into AI-powered Treasury Ops, Composable Finance, and Smart Lending Stacks. Stay tuned.
Data References:
We’ll continue to update this series with future frameworks, including Smart Treasury Ops, AI-led Lending Journeys, and Composable Banking Models. Until then, follow us for deeper insights into India’s fintech infrastructure.